In the coming years, organisations will face a fast-evolving threat landscape. Cybercriminals continue to refine their techniques, increasing pressure on security teams to adapt quickly. At the same time, global cybercrime damages are projected to reach USD 15.6 trillion by 2029.
This surge in risk is driving higher investment, with Gartner estimating worldwide end-user spending on information security to hit USD 213 billion in 2025 and about USD 240 billion in 2026.
New technologies add further complexity, while the shortage of skilled cybersecurity professionals makes it harder for organisations to keep pace.
Opportunities on the horizon
Despite these challenges, AI, GenAI and ML are creating new defensive possibilities through faster detection, better insights and more automated protection. Gartner reports that by 2027, around 17% of cyberattacks and breaches will involve GenAI. A 2025 survey also shows that 69% of organisations believe employees are using unauthorised public GenAI tools, with more than 40% expected to face shadow-AI incidents by 2030. This pushes vendors to strengthen governance, data controls and AI-driven security capabilities across cloud and hybrid environments.
As digital systems become more identity-centric, PKI is also gaining renewed importance. Organisations are preparing for post-quantum cryptography, and PKI vendors are expanding support for automation, crypto-agility and quantum-safe options to secure long-term trust across cloud, IoT and AI-driven environments.
Who are the top cybersecurity companies in 2026?
To address these challenges and seize new opportunities, cybersecurity vendors must innovate, attract skilled talent and integrate emerging technologies into their platforms. In this article, we review notable developments from several companies in 2025, highlighting key advancements shaping the industry in 2026.
Palo Alto Networks
Palo Alto Networks remains one of the strongest global players in cybersecurity. The company serves more than 80,000 customers, including most Fortune 100 organisations and a large share of the Global 2000. Its portfolio spans network security, SASE, cloud security and AI-driven threat protection.
Key milestones
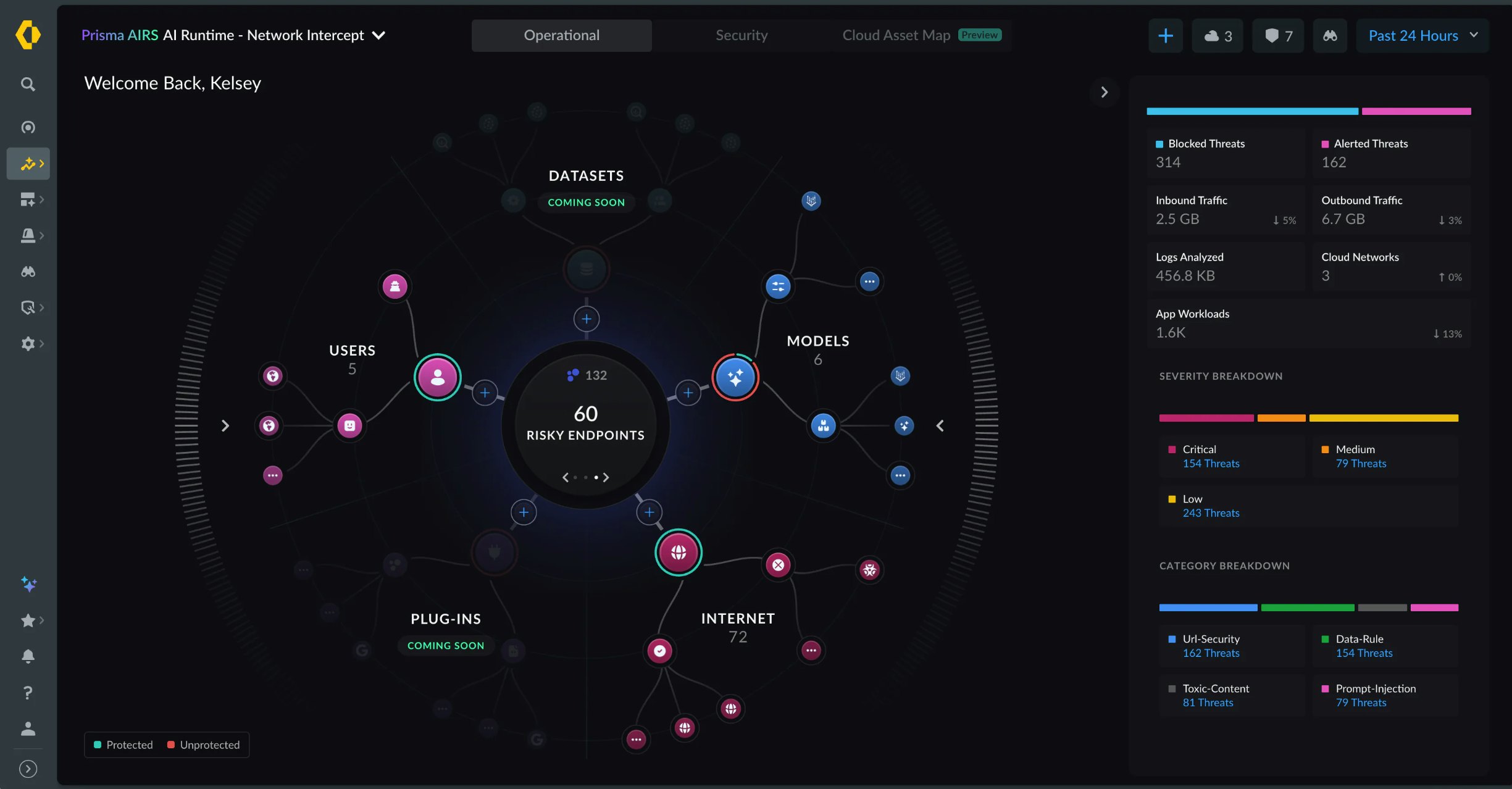
In April 2025, the firm launched Prisma Access Browser 2.0, described as the first “SASE-native secure browser.” It aims to extend SASE protections directly into the browser as enterprises increasingly rely on cloud applications, BYOD and SaaS tools. In 2025, the company accelerated its shift toward AI-native security across its platforms. Prisma SASE 4.0 introduced AI-driven threat protection, data controls for SaaS and AI-agent usage, and unified cloud operations aimed at reducing complexity in hybrid environments. Prisma AIRS 2.0 expanded this further by securing the full lifecycle of enterprise AI applications, covering model inspection, agent behaviour and continuous testing.
Palo Alto also advanced its position in secure access and modern work environments with the Prisma Access Browser 2.0. These developments supported strong analyst recognition. The company was named a Leader in the Gartner Magic Quadrants for SASE Platforms, Security Service Edge (SSE) and the inaugural Hybrid Mesh Firewall Magic Quadrant, highlighting its breadth across network, cloud and access-security domains.
Strategic acquisitions
Palo Alto Networks expanded its capabilities in 2025 through three key acquisitions:
- Protect AI (closed July 2025): Strengthens security for AI and machine-learning pipelines.
- CyberArk (announced July 2025): Expands identity-security and privileged-access capabilities.
- Chronosphere (announced November 2025, expected to close fiscal 2026): Adds cloud-native observability and telemetry to support platform integration.
Fortinet
Fortinet remains a major global player in cybersecurity, offering an integrated platform that protects networks, cloud environments and distributed users. Its portfolio serves large enterprises, service providers and public-sector organisations looking for consistent security across complex infrastructures.
Key milestones
In 2025, Fortinet advanced its focus on AI-driven security. The company introduced new Secure AI Data Center capabilities designed to protect AI models, datasets and supporting infrastructure, reflecting the growing need for dedicated AI-era protection. Fortinet also expanded automation across its Security Fabric, improving detection and response across cloud, LAN and WAN environments.
During the year, Fortinet strengthened its position in hybrid and multicloud security, adding deeper integration with major cloud providers and enhancing Secure Access and Security Operations capabilities. Independent evaluations also highlighted continued customer adoption of Fortinet’s integrated approach, including recognition of its SD-WAN and SASE capabilities in the analyst landscape. They can also be found in the SASE and Hybrid Mesh Firewall Magic Quadrant presented by Gartner in 2025.
Strategic acquisitions
In 2025, Fortinet strengthened its cybersecurity capabilities with three key acquisitions:
- Perception Point(acquired December 2024): Added advanced email and collaboration-security capabilities, strengthening Fortinet’s protection against phishing and content-based attacks.
- Suridata.ai(acquired May 2025): Improved SaaS security posture management by adding AI-driven visibility, governance and risk controls across cloud applications.
- Everest Networks(acquired May 2025): Enhanced Fortinet’s secure wireless and edge portfolio with high-performance Wi-Fi and analytics technology for large and distributed environments.
Zscaler
Zscaler remains a major provider of Zero Trust and cloud-delivered security, protecting users, workloads and devices across distributed and multi-cloud environments through its Zero Trust Exchange platform.
Key milestones
In 2025 Zscaler expanded its Zero Trust capabilities with new platform updates aimed at securing branch, campus and cloud environments without relying on traditional network architectures. The company introduced new Zero Trust Branch functionality, giving organisations a way to segment IoT and OT devices and modernise legacy network designs while maintaining consistent Zero Trust policies across locations.
Zscaler also advanced its AI-driven security features with improved data classification and prompt inspection to support safe use of generative AI and cloud applications. The company continued to gain analyst recognition during the year, being named a Visionary in the 2025 Gartner Magic Quadrant for SASE Platforms and a Leader in the 2025 Forrester Wave for SASE Solutions.
Strategic acquisitions
To further strengthen its Zero Trust and AI-security portfolio, Zscaler made two key acquisitions in 2025:
- Red Canary (acquired August 2025): Added advanced MDR capabilities and threat-intelligence expertise to strengthen detection and response within Zscaler’s platform.
- SPLX (acquired November 2025): Brought AI-security tooling for model discovery, testing and runtime protection, extending Zscaler’s coverage across the full AI lifecycle.
CrowdStrike
Founded in 2011, CrowdStrike has become a leading player in the cybersecurity industry. The company’s flagship product, the CrowdStrike Falcon platform, is widely recognised for its effectiveness in defending organisations against advanced cyber threats.
The 2024 global outage caused by a faulty update still shapes CrowdStrike’s reputation in 2026. The company spent much of 2025 rebuilding trust, investing in stricter software testing, automated validation pipelines and expanded safeguards across Falcon updates. For enterprises, this translated into clearer transparency, more predictable update cycles and improved rollback controls. The firm maintained strong momentum despite the incident, with customer growth and recurring revenue remaining solid through 2025.
Key milestones
In 2025, CrowdStrike expanded the Falcon platform with new AI-native capabilities. The Falcon Fall Release introduced an AI-ready data layer and the Enterprise Graph, combining telemetry and threat intelligence into a unified model to accelerate detection and investigation.
The company also advanced its automation strategy with Charlotte AI, enabling faster analysis and scalable response as adversaries adopt automated attack techniques. CrowdStrike strengthened coverage across identity, cloud and SaaS environments, positioning Falcon as a unified security backbone beyond endpoints.
The vendor again appeared as a Leader in Gartner’s Endpoint Protection Platforms evaluations and maintained strong customer satisfaction ratings.
Strategic acquisitions
To expand its capabilities, CrowdStrike made two notable acquisitions in 2025:
- Onum(announced August 2025): Added real-time telemetry pipeline capabilities to improve Falcon’s next-gen SIEM performance and speed up detection.
- Pangea(announced September 2025): Brought AI-security controls across data, models and agents, supporting CrowdStrike’s new AI Detection and Response capabilities.
Get in touch with our security experts
Our European team is available for a quick call or video meeting. Let's connect and discuss your security challenges, dive into vendor comparison reports, or talk about your upcoming IT projects. We are here to help.

HPE
HPE emerged as a new combined entity in 2025 following Hewlett Packard Enterprise’s acquisition of Juniper Networks. The deal brought together Juniper’s security stack, firewalls and AI-driven operations with Aruba’s secure access, NAC and edge-security portfolio. By uniting these two ecosystems, HPE is positioning itself as a stronger competitor in the enterprise networking and security market, offering organisations a more integrated security foundation across campus, branch, data-centre and cloud environments.
Key milestones
In 2025, HPE expanded its Secure Service Edge (SSE) capabilities by extending secure access, Zero Trust enforcement and network access control (NAC) across a broader range of environments. Aruba’s NAC and secure access technologies are being aligned with Juniper’s security and policy framework to support identity-driven access, device trust and more consistent security enforcement across distributed networks. This strengthens HPE’s position in Zero Trust and SSE for organisations managing hybrid users, cloud workloads and unmanaged devices.
HPE also introduced a new generation of Juniper SRX firewalls in 2025, refreshing its core next-generation firewall portfolio. The new SRX platforms extend enterprise-grade threat prevention, secure segmentation and high-performance inspection across campus, data-centre and cloud-edge deployments. These firewalls are positioned as part of HPE’s long-term secure infrastructure strategy, with support for modern encryption standards and preparation for future cryptographic requirements, including quantum-resilient options.
Alongside these security updates, HPE introduced new agentic AI-native enhancements for Mist during the year, improving autonomous operations, troubleshooting and visibility across wired, wireless, WAN and data-centre environments. These updates lay the groundwork for closer alignment of policy management, access control and automation across the combined portfolio as consolidation progresses.
Further integration is expected in 2026 as HPE continues aligning Juniper’s AI-native operations with Aruba’s secure access capabilities, bringing the two portfolios closer together to support a more consistent and resilient network security architecture.
F5
F5 is a key provider of application and security services for enterprises operating across hybrid and multicloud environments. Its portfolio focuses on protecting modern applications, APIs and AI-driven workloads, while supporting consistent performance and visibility across distributed infrastructures.
Key milestones
In 2025, F5 expanded its focus on securing AI-centric and containerised environments. The company advanced its BIG-IP Next for Kubernetes offering, adding support for AI-accelerated infrastructure to improve application security and delivery for organisations deploying AI workloads across hybrid cloud. F5 was also recognised on the 2025 CRN AI 100 list, highlighting its role in supporting emerging AI-driven data-centre and edge-networking requirements.
The year also brought security challenges. In October 2025 F5 disclosed a breach involving unauthorised access to parts of its internal network, including source code and information related to BIG-IP products. The company issued patches and security notifications across BIG-IP, F5OS and cloud components to mitigate potential risks. Alongside this response, F5 continued to emphasise future-facing technologies such as WebAssembly (Wasm), framing it as a strategic component for secure and portable application delivery in hybrid environments.
Strategic acquisitions
To further expand its cybersecurity capabilities, F5 made two key acquisitions in 2025:
- Fletch (acquired June 2025): Agent-based AI startup whose technology helps F5’s platform surface high-value security signals and reduce alert noise.
- MantisNet (acquired August 2025): Added cloud-native, eBPF-based observability to strengthen real-time network telemetry and visibility within F5’s Application Delivery and Security Platform.
- CalypsoAI (acquired September 2025): Brought AI-security guardrails for monitoring and protecting AI models and agents, enhancing F5’s ability to secure enterprise AI workloads.
Cisco
Cisco is a global leader in networking and cybersecurity, serving a diverse range of customers, including numerous Fortune 500 companies. The company provides a comprehensive portfolio of security technologies, including Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) and Zero Trust solutions, tailored to meet the needs of large enterprises.
Key cybersecurity milestones
In 2025, Cisco advanced its security strategy with new AI-driven capabilities across Cisco Security Cloud. Announced at RSAC 2025, these updates focused on defending against AI-powered threats, improving detection accuracy and strengthening protection across hybrid and multicloud environments.
Cisco also expanded Security Cloud Control with enhanced multi-customer management, giving MSPs and large enterprises a more unified and scalable way to manage Secure Access, Hybrid Mesh Firewall and related services.
Strategic acquisitions
Cisco expanded its cybersecurity portfolio in late 2024 and in 2025 with several key acquisitions:
- SnapAttack (acquired late 2024, integrated through 2025): A threat-detection and adversary-emulation platform that enhances Cisco’s detection engineering, behavioural analytics and proactive defence capabilities within Cisco Security Cloud.
- NeuralFabric (intent to acquire November 2025): An enterprise AI platform that supports Cisco’s move toward AI-native security by improving model orchestration and accelerating AI-driven protection across hybrid and multicloud environments.
Noteworthy cybersecurity companies for 2026
As we move into 2026, a handful of companies are quietly shaping how digital trust works under the hood: DigiCert, Keyfactor and Thales. Together, they’re tackling some of the hardest problems in modern cybersecurity, from managing exploding volumes of certificates to preparing for the post-quantum world.
Alongside them, Tenable continues to define the exposure-management space, helping organisations understand and reduce cyber-risk across increasingly complex hybrid environments.
DigiCert
DigiCert has become one of the key names in digital trust, with a cloud-delivered, SaaS-based platform for managing digital certificates across cloud, IoT and traditional enterprise environments. Instead of running their own PKI stacks, many organisations now consume certificate lifecycle management as a service, integrating DigiCert’s APIs into CI/CD pipelines, device onboarding and identity workflows.
Combined with its work on post-quantum-ready (quantum-safe) certificates, this SaaS-first approach puts DigiCert at the centre of identity-centric security and crypto-agility: knowing what you’re using, being able to swap algorithms, and doing it all at scale without owning all the plumbing.
Thales
Thales operates at the deeper layers of technology, focusing on the cryptographic foundations themselves. As a European company, Thales also plays a significant role in supporting digital sovereignty for organisations within Europe, ensuring that sensitive cryptographic functions and key material can be managed within European jurisdictions.
Thales’ hardware security modules (HSMs) and key-management platforms are widely used by governments, banks and critical infrastructure operators to protect keys, transactions and sensitive data.
As quantum threats shift from theory to roadmap, Thales’ investments in post-quantum cryptography and secure key protection position the company as a strategic long-term partner. Its technology underpins essential trust functions within large organisations, anchoring data-centric security across digital infrastructure.
Keyfactor
Keyfactor, meanwhile, has carved out a strong position in machine identity management and PKI automation, with a deliberate focus on both on-premises and SaaS deployments. Regulated enterprises can run Keyfactor in their own data centres, close to HSMs and sensitive workloads, while others opt for fully managed cloud services – or a hybrid of the two. As certificates proliferate across cloud platforms, DevOps pipelines, IoT fleets and containerised environments, outages caused by expired or misconfigured certificates are becoming a real operational risk.
Their focus on visibility, automation and policy-driven control helps enterprises keep that complexity in check. Its emphasis on crypto-agility and post-quantum readiness aligns with what many security teams are now prioritising: being able to adapt their cryptography without having to rebuild everything from scratch.
Tenable
Tenable remains a key vendor for organisations working to reduce cyber-risk as cloud, identity and AI-driven workloads expand. Its continuous exposure-management approach helps teams understand how vulnerabilities, misconfigurations and identity gaps combine across hybrid environments. In 2025, Tenable gained further analyst recognition as a Leader in Gartner’s Magic Quadrant for Exposure Assessment Platforms, reinforcing its role in helping organisations prioritise remediation and navigate increasingly complex infrastructures.
Nomios’ cybersecurity vendors
The vendors we work with form the backbone of our cybersecurity architecture, empowering our customers to transition seamlessly to Zero Trust Access, Secure Services Edge (SSE) and Secure Access Service Edge (SASE). By combining the technologies of these leading cybersecurity companies with Nomios’ local expertise, we help organisations build security architectures that fit their needs.
Alongside design and integration, we deliver managed security services such as Managed Detection and Response (MDR), supported by our own SOC. This approach maximises security, reduces operational overheads and supports a smooth user experience across the organisation.
Every organisation is unique, and the ideal solutions for 2026 depend on specific requirements. At Nomios, we’re committed to helping you identify and implement the cybersecurity approach that best supports your goals and challenges.
Do you want to know more about this topic?
Our experts and sales teams are at your service. Leave your contact information and we will get back to you shortly.